[ch3] 7. TCP congestion control
1. Key Questions
- congestion control를 하고 싶다!
- congestion이 있으면 처리속도를 내림
- congestion이 없다면 처리속도를 올림
- Key questions
- 'rate'를 제어하는 방법?
- congestion을 감지하는 방법?
- rate를 얼마나 증감시키켜야 하는가? rate를 언제 증감시켜야 하는가
- TCP Reno에서의 congestion control 방법을 살펴볼 것
2. TCP's congestion control: keywords
- Key states & mechanisms
- slow start
- congestion avoidance: AIMD
- AIMD: Additive Increase Multiplicative Decrease
- fast recovery
- Key parameters
- congestion window: cwnd
- slow-start threshold: ssthresh
- MSS, RTT
- Key events
- ACK received
- timeout
- 3 duplicate ACK received
3. TCP Congestion Window
- 송신자는 전송을 제한함
- LastByteSent - LastByteAcked <= cwnd
- cwnd= 허용 가능한 outstanding frame 수
- TCP의 congestion control은 cwnd, 즉 윈도우 사이즈를 제어하는 것임
- cwnd는 동적임
- TCP 전송률 = cwnd/RTT bytes/sec
- cwnd bytes를 전송
- ACKs에 대한 RTT를 기다림
- 더 많은 바이트를 보냄
4. TCP Slow Start
- 연결이 시작되고, 첫번째 loss가 발생할 때까지 rate를 exponential하게 높혀라
- 처음 cwnd = 1 MSS
- 매 RTT마다(ACK를 받을 때마다) cwnd를 두 배로 증가시킴
- 초기 속도는 느리지만 엄청 빨라짐
- timeout event가 발생될 때마다 'slow start' state로 돌아옴
- 3 dup ACK이 발생할 때마다 'congestion avoidance' state로 가라
5. TCP: detecting congestion, reacting to loss
- packet loss를 토대로 congestion 감지
- loss는 timeout 또는 3 duplicate ACK로 알 수 있음
- timeout에 의한 loss
- 'slow start' state로 가라
- cwnd는 1로 설정됨
- 윈도우는 ssthresh까지 exponentially하게 증가함
- ssthresh에 도달하면 linearly하게 증가
- 'congestion avoidance' state로 감
- 3 dup ACK에 의한 loss
- dup ACK는 네트워크가 그래도 segment를 전송할 수 있다는 것을 의미
- cwnd를 반으로 줄임
- 그 다음 linearly하게 증가
- 'congestion avoidance' state로 감
- TCP Reno, TCP New Reno에서 사용
6. TCP congestion avoidance: AIMD
- 접근: 송신자는 loss가 발생할 때까지 전송률을 증가시키고 사용가능한 bandwidth가 있는지 알아봄
- additive increase: loss가 발견될 때까지 매 RTT 마다 1 MSS 만큼 cwnd를 증가함
- multiplicative decrease: loss가 발견되면 cwnd를 반으로 자름
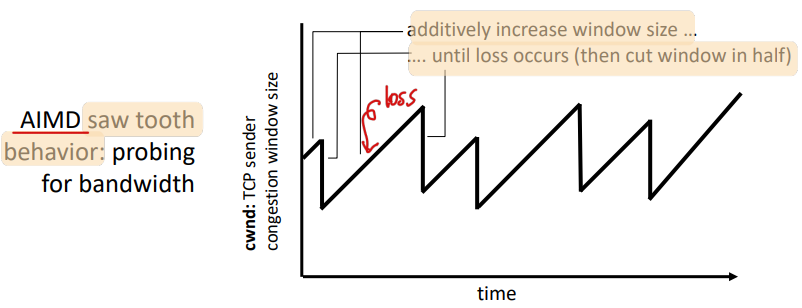
7. TCP: switching from slow start to CA
- Q: exponential incresase switch가 언제 linear하게 바뀌어야함?
- A: timeout 전에 cwnd가 1/2로 깎일 때. ssthresh를 이용해 구현
- loss event에서 ssthresh는 loss event가 발생하기 직전에 cwnd의 1/2로 설정됨

8. Summary: TCP Congestion Control

- Slow Start
- 다른 state에서 timeout 발생시 이 state로 옴
- initial state
- cwnd=1 MSS, ssthresh = 64KB, dupACKcount = 0으로 설정
- new ACK
- cwnd = cwnd+MSS, dupACKcount = 0
- 새로운 segment 전송
- dupclicate ACK
- timeout
- ssthresh를 cwnd의 1/2로 cut
- cwnd = 1 MSS
- dupACKcount = 0
- missing segment 재전송
- dupACKcount == 3
- ssthresh를 cwnd의 1/2로 cut
- cwnd = ssthresh + 3
- 왜 3을 더하는가? 3 dupACK를 받았기 때문에 3개를 더 보내야 함
- missing segment 재전송
- Congestion Avoidance
- slow start에서 cwnd가 ssthresh보다 커지면 이 state로 옴
- new ACK
- cwnd = cwnd + MSS * (MSS/cwnd)
- MSS/cwnd = 매 RTT 당 하나의 MSS 추가 --> addivitve increase
- dupACKcount = 0
- 새로운 segment 전송
- duplicate ACK
- dupACKcount == 3시, fast recovery state로 감
- ssthresh=cwnd/2
- cwnd = ssthresh + 3
- missing segment 재전송
- timeout 발생시, slow state로 감
- ssthresh = cwnd/2
- cwnd = 1 MSS
- dupACKcount = 0
- missing segment 재전송
- fast recovery
- duplicate ACK
- cwnd = cwnd + MSS
- 중간에 한 packet이 loss 되었다고 나는 멈추고 싶지 않다~~~
- 새 segment 전송
- New ACK
- congestion avoidance state로 감
- cwnd = ssthresh
- dupACKcount = 0
- timeout
- slow start state로 감
- ssthresh = cwnd/2
- cwnd = 1
- dupACKcount = 0
- missing segment 재전송
9. TCP throughput
- 평균 TCP throughput은 윈도우 사이즈와 RTT에 관한 식으로 나타낼 수 있음
- slow start 무시, 항상 데이터가 전송된다고 가정
- W: loss가 일어났을 때의 window size
- 평균 window size는 3/ * 4W
- 평균 throughput은 RTT 당 3/4 * W
- 평균 TCP throughput = 3/4 * W/RTT * bytes/sec
10. TCP Futures: TCP over "long, fat pipes"
- 예시)
- 1500 bytes segments
- 100ms RTT
- 10 Gbps throughput을 원함
- segment loss 확률에 관한 throughput
- TCP throughput = 1.22 * MSS / (RTT * sqrt(L))
- 10 Gbps throughput을 얻기 위해서, L = 2*10^(-10)의 loss rate가 필요
11. TCP Fairness
- 목표: K개의 TCP sessions이 bandwidth가 R인 같은 bottleneck link를 공유하고 있다면, 각각은 R/K의 평균 rate를 가져야 함. 어느 하나가 rate를 엄청 높이면 안됨 (should not be selfish / greedy)
- TCP의 AIMD algorithm은 fair한가?

- Fairness, parallel TCP connections
- app은 두 호스트 간에 여러 개의 parallel connection을 열 수 있음
- web browsers은 이것을 지원함
12. Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN)
- network-assisted congestion control
- network의 router에 의해 표시되는 IP header의 두 bit로 congestion을 나타냄
- congestion 지표는 receiving host로 전송됨
- 수신자는 IP datagram의 congestion indication을 보고 송신자에게 congestion을 알리기 위해 ACK segment의 ECE bit를 set함.
13. Extra
- RDT와 Congestion control은 서로 관계가 있다 (not independent)
- UDP의 app layer에서 RDT와 CC를 구현할 수 있음
- DCCP (Datagram Congestion Control Protocol)
- Google's QUIC
- DCTCP, SCTP, TRFC 등
- OS나 라우터를 바꾸는 것 없이 TCP보다 나은 성능을 가지는 것을 목표로 함
- TCP는 TCP-friendly해야 해서 일정 속도 이상으로 전송속도를 올릴 수 없음
- TCP friendliness
- transport layer protocol을 디자인할 때, greedy하게 디자인하면 안됨






댓글